Signs Of A Gambling Problem
Gambling Disorder is behavior which causes disruptions in any major area of life: psychological, physical, social or vocational. It is a progressive addiction characterized by increasing preoccupation with gambling, a need to bet more money more frequently, restlessness or irritability when attempting to stop, “chasing” losses, and loss of control manifested by continuation of the gambling behavior in spite of mounting, serious, negative consequences.
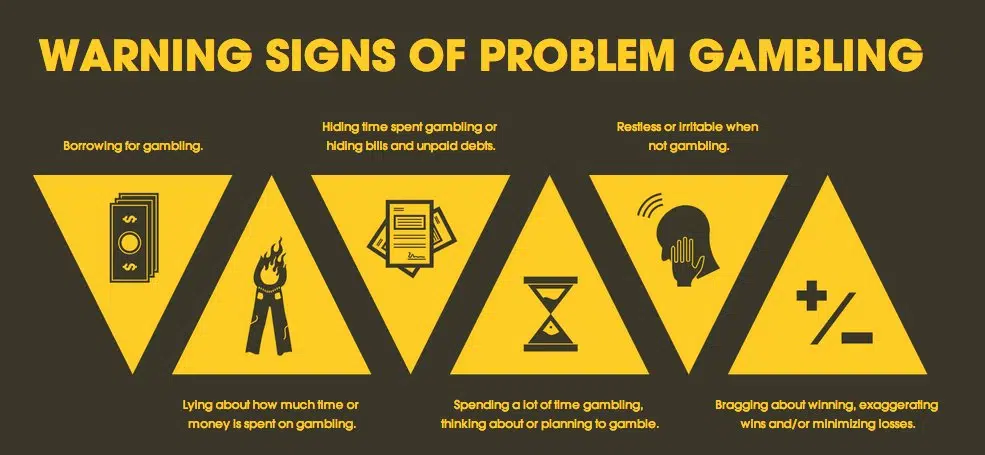
Signs of a Gambling Disorder:
A person shows signs of gambling disorder if he/she:
The NMCPG recommends concerned parents to consider all the warning signs of a potential gambling problem in addition to other variables that may be influencing changes in their child’s behavior. If answering these questions leads you to believe a gambling problem exists, seek immediate help to obtain effective resources and awareness on. Gambling Addiction: Signs, Symptoms and Rehab Treatment. Gambling addiction – also known as “problem” or “compulsive gambling” – is the condition of feeling compelled to gamble, and/or gamble excessive amounts, despite an awareness of the negative consequences of doing so and the desire to stop.
- Needs to gambling with increasing amounts of money to achieve the desired excitement
- Exhibits restless or irritable behavior when attempting to cut down or stop gambling
- Is often preoccupied with thoughts about gambling
- Often gambles when feeling distress
- Chase’s ones losses/returns another day to get even
- Lies to conceal the extent of gambling
- Jeopardizes a significant relationship, job or opportunity because of gambling
- Relies on others to provide money to relieve desperate financial situations caused by gambling
Disordered gambling rates:

Research estimates that approximately 2% (83,200-135,100) of the Massachusetts adult population has a gambling disorder
At-Risk gambling rate:
Warning Signs Of Gambling Disorder
Research estimates that approximately 8.4% (389,700-488,500) of Massachusetts adults are at-risk gamblers, demonstrating gambling behaviors that put them at risk of developing a gambling disorder.